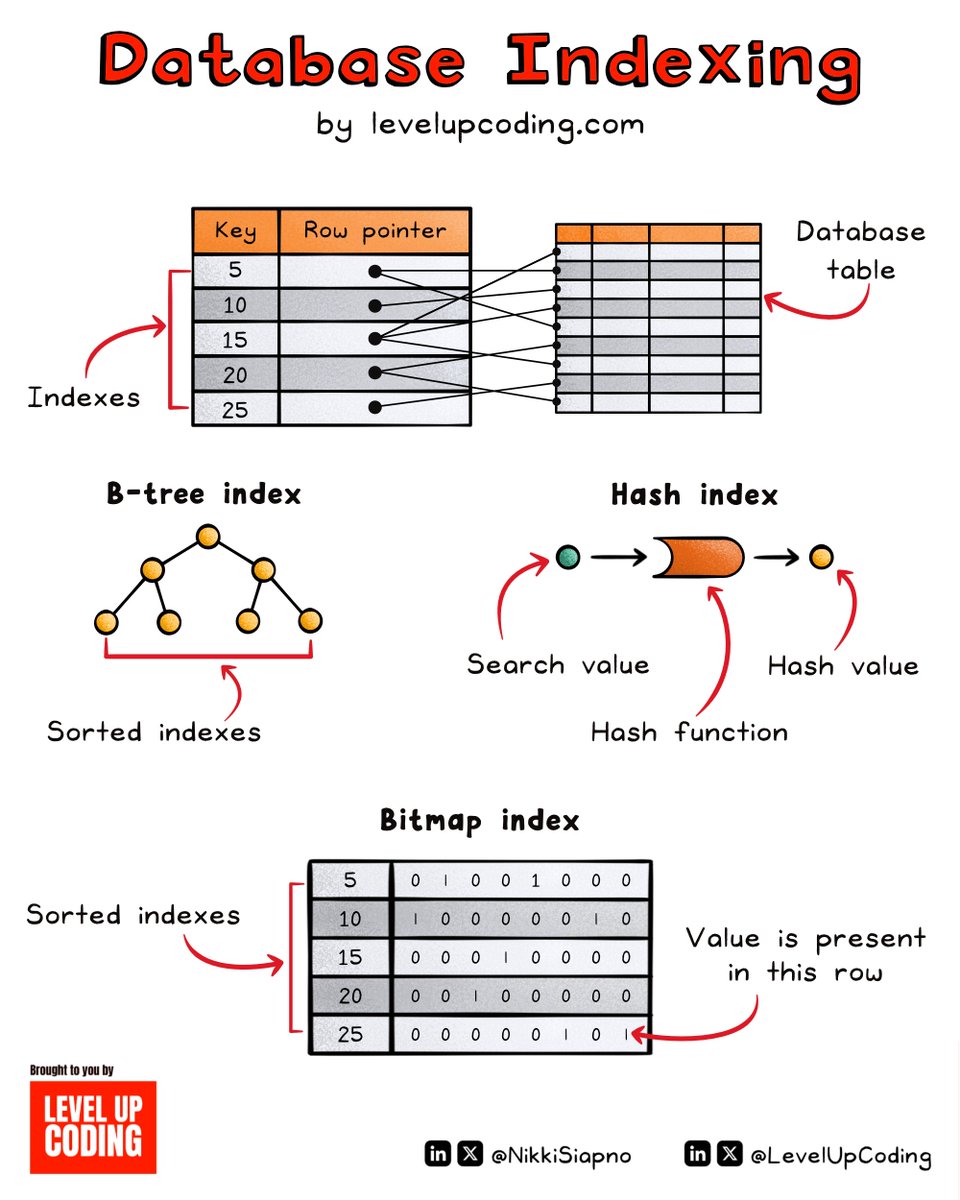
Database indexing clearly explained. A database index is a lot like the index on the back of a book. It saves you time and energy by allowing you to easily find what you're looking for without having to flick through every page. Database indexes work the same way. An index is a key-value pair where the key is used to search for data instead of the corresponding indexed column(s), and the value is a pointer to the relevant row(s) in the table. Most databases require some form of indexing to keep up with performance benchmarks. To get the most out of your database, you should use the right index type for the job. The 𝗕-𝘁𝗿𝗲𝗲 is one of the most commonly used indexing structures where keys are hierarchically sorted. When searching data, the tree is traversed down to the leaf node that contains the appropriate key and pointer to the relevant rows in the table. B-tree is most commonly used because of its efficiency in storing and searching through ordered data. Their balanced structure means that all keys can be accessed in the same number of steps, making performance consistent. 𝗛𝗮𝘀𝗵 𝗶𝗻𝗱𝗲𝘅𝗲𝘀 are best used when you are searching for an exact value match. The key component of a hash index is the hash function. When searching for a specific value, the search value is passed through a hash function which returns a hash value. That hash value tells the database where the key and pointers are located in the hash table. 𝗕𝗶𝘁𝗺𝗮𝗽 𝗶𝗻𝗱𝗲𝘅𝗶𝗻𝗴 is used for columns with few unique values. Each bitmap represents a unique value. A bitmap indicates the presence or absence of a value in a dataset, using 1’s & 0’s. For existing values, the position of the 1 in the bitmap shows the location of the row in the table. Bitmap indexes are very effective in handling complex queries where multiple columns are used. When you are indexing a table, make sure to carefully select the columns to be indexed based on the most frequently used columns in WHERE clauses. A 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗼𝘀𝗶𝘁𝗲 𝗶𝗻𝗱𝗲𝘅 may be used when multiple columns are often used in a WHERE clause together. With a composite index, a combination of two or more columns are used to create a concatenated key. The keys are then stored based on the index strategy, such as the options mentioned above. Indexing can be a double-edged sword. It significantly speeds up queries, but it also takes up storage space and adds overhead to operations. Balancing performance & optimal storage is crucial to get the most out of your database without introducing inefficiencies. 💭 Over to you. What would you add? 💬 ~~ Thanks to our partner Udacity who keeps our content free to the community. 𝗪𝗮𝗻𝘁 𝘁𝗼 𝗯𝘂𝗶𝗹𝗱 𝗔𝗜 𝘀𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝘀 𝘁𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗴𝗼 𝗯𝗲𝘆𝗼𝗻𝗱 𝗷𝘂𝘀𝘁 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝗺𝗽𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴? Learn to design, orchestrate, and deploy agentic AI with Udacity’s new program. Check it out here: